Carotid Interventions
Home - Carotid Interventions
Carotid interventions are minimally invasive procedures designed to treat carotid artery disease, a condition where the carotid arteries, the major blood vessels supplying blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked. These procedures are crucial for preventing strokes and improving blood flow to the brain, thus safeguarding overall cerebral health.
Understanding Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the carotid arteries, leading to a condition known as atherosclerosis. This buildup can restrict blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of stroke, which can have devastating consequences.
Causes of Carotid Artery Disease
- Atherosclerosis: The primary cause, where plaque buildup narrows the arteries.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure damages the arterial walls, promoting plaque formation.
- Smoking: Increases the risk of atherosclerosis and accelerates the progression of carotid artery disease.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels contribute to arterial damage and plaque buildup.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol lead to plaque deposits in the arteries.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease often progresses without noticeable symptoms until it becomes severe. However, warning signs of a possible stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) may include:
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: Particularly on one side of the body.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech: Sudden trouble with language can indicate a TIA or stroke.
- Vision Problems: Sudden loss of vision in one eye or both.
- Dizziness or Loss of Balance: Unexplained dizziness or coordination issues.
- Severe Headache: Sudden, intense headache with no known cause.
Types of Carotid Interventions
Carotid interventions aim to restore adequate blood flow to the brain and prevent stroke. The two primary types of carotid interventions are:
Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
- Procedure Overview: Carotid endarterectomy involves a surgical incision in the neck to access the carotid artery. The surgeon removes the plaque buildup from the artery walls, restoring normal blood flow.
- Benefits: Highly effective in reducing the risk of stroke in patients with significant carotid artery stenosis (narrowing).
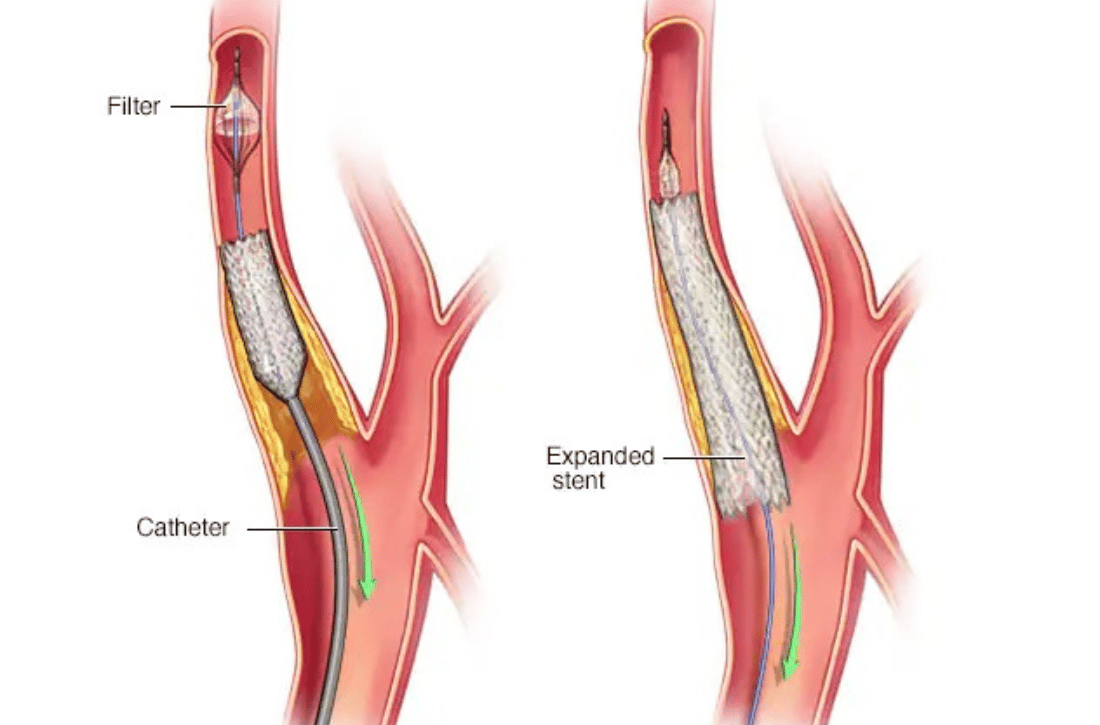
Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS)
- Procedure Overview: Carotid artery stenting is a less invasive procedure where a small mesh tube (stent) is inserted into the carotid artery to keep it open. The stent is placed using a catheter inserted through a small incision in the groin.
- Benefits: Suitable for patients who are high-risk surgical candidates. It offers quicker recovery and less discomfort compared to carotid endarterectomy.
Detailed Procedure: Carotid Artery Stenting
Pre-Procedure Preparation
- Diagnostic Imaging: Ultrasound, CT angiography, or MR angiography to evaluate the extent of carotid artery disease and plan the procedure.
- Medical Assessment: Thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to ensure suitability for the procedure.
- Medication Review: Assessment of current medications, including blood thinners, to reduce the risk of complications.
Procedure Steps
- Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia is administered at the catheter insertion site, typically in the groin.
- Catheter Insertion: A small incision is made to insert the catheter into the femoral artery, which is guided to the carotid artery under fluoroscopic guidance.
- Angioplasty: A balloon catheter is used to widen the narrowed segment of the carotid artery.
- Stent Placement: A stent is positioned at the site of the narrowing and expanded to keep the artery open, ensuring improved blood flow to the brain.
- Post-Procedure Monitoring: After the stent is placed, the catheter is removed, and the insertion site is closed. The patient is monitored for any immediate complications.
Post-Procedure Care
- Hospital Stay: Most patients require an overnight stay for observation and monitoring of vital signs and neurological status.
- Medications: Prescription of antiplatelet medications to prevent blood clots and promote healing of the treated artery.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits to assess the success of the intervention, monitor for restenosis, and address any ongoing symptoms.
Benefits of Carotid Interventions
- Stroke Prevention: Significant reduction in the risk of stroke in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis.
- Minimally Invasive Options: Carotid artery stenting offers a less invasive alternative to surgery with quicker recovery times.
- Symptom Relief: Alleviates symptoms such as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are warning signs of potential strokes.
- Improved Quality of Life: Enhanced blood flow to the brain reduces the risk of stroke-related disabilities and improves overall health.
Conclusion
Carotid interventions, including carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting, are crucial procedures for managing carotid artery disease and preventing strokes. Dr Ankeet Dedhiya and our team of experienced vascular specialists and interventional cardiologists are dedicated to providing personalized, state-of-the-art care to improve your vascular health and reduce your stroke risk. Whether you are undergoing diagnostic evaluation or preparing for a carotid intervention, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Carotid interventions are medical procedures designed to treat carotid artery disease, which involves narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. These interventions help restore adequate blood flow to the brain and reduce the risk of stroke.
Carotid interventions are recommended for patients with significant carotid artery stenosis (narrowing), especially those who have experienced symptoms like transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or minor strokes. They may also be considered for patients with asymptomatic severe carotid stenosis.
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA): A surgical procedure where an incision is made in the neck to remove plaque buildup from the carotid artery.
- Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS): A minimally invasive procedure where a stent is placed in the carotid artery via a catheter inserted through a small incision in the groin, helping to keep the artery open.
Carotid artery disease is typically diagnosed using imaging studies such as carotid ultrasound, CT angiography, or MR angiography. These tests help visualize the extent of plaque buildup and narrowing in the carotid arteries.
While generally safe, carotid interventions carry some risks, including:
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) during the procedure.
- Bleeding at the catheter insertion site.
- Arterial dissection (tearing of the artery wall).
- Restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery).
- Infection at the insertion site or within the treated vessel.
Recovery time varies depending on the type of intervention. Carotid endarterectomy may require a hospital stay of 1-2 days, while carotid artery stenting usually involves an overnight stay. Most patients can return to normal activities within a week, but complete recovery may take longer.
During the recovery period, patients should:
- Follow prescribed medications, especially antiplatelet drugs to prevent blood clots.
- Attend follow-up appointments to monitor the success of the intervention and check for restenosis.
- Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few weeks.
- Monitor the insertion site for any signs of infection, bleeding, or swelling.
While certain risk factors like age and family history cannot be controlled, you can reduce your risk of developing carotid artery disease by:
- Quitting smoking.
- Managing chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine.
- Regularly monitoring your cardiovascular health with your healthcare provider.
Yes, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can help prevent further artery disease and maintain the success of the intervention:
- Eat a balanced diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Exercise regularly to maintain cardiovascular health.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, hobbies, or counseling.
Carotid interventions, particularly for patients with significant stenosis, are highly effective in reducing the risk of stroke. Carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting have both been shown to significantly lower the incidence of stroke in appropriately selected patients.
Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor the success of the procedure and detect any signs of restenosis. Your healthcare provider will schedule imaging tests and physical examinations to ensure that the treated artery remains open and that your risk of stroke is minimized.
