Rotational Atherectomy
Home - Rotational Atherectomy
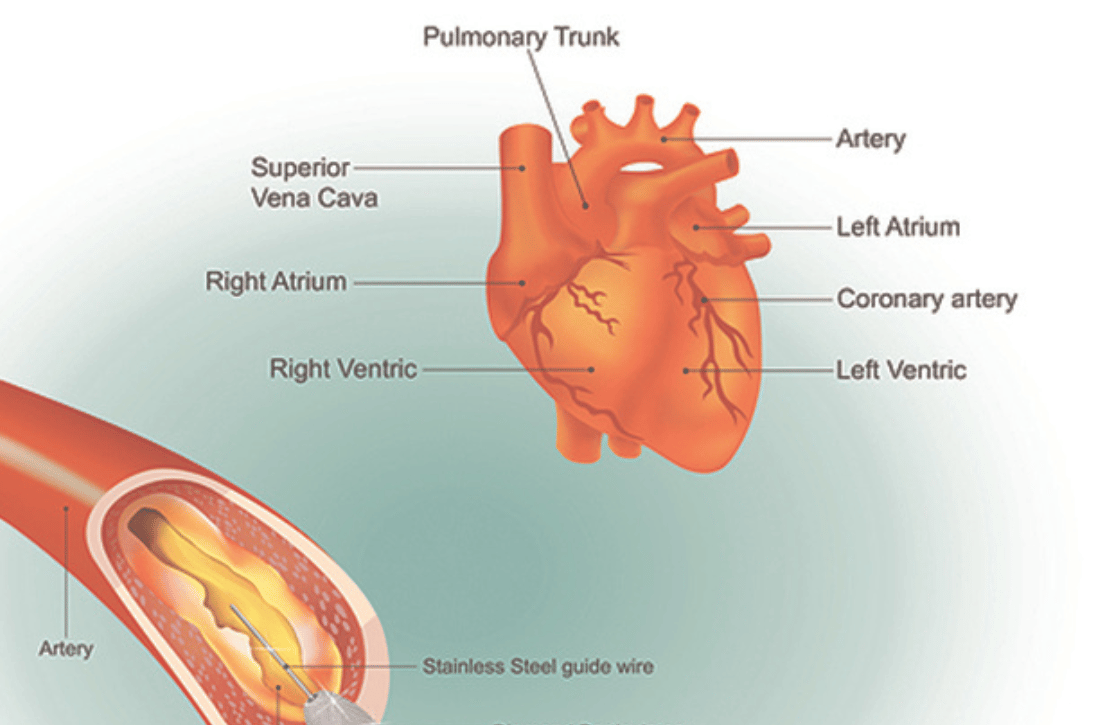
Rotational Atherectomy is an advanced interventional cardiology procedure used to treat severely calcified coronary arteries that are difficult to dilate with traditional angioplasty techniques. This procedure involves using a specialized device to physically remove calcified plaque from the artery walls, restoring blood flow and optimizing the success of subsequent treatments such as angioplasty and stent placement.
Understanding Coronary Artery Calcification
Coronary artery calcification occurs when calcium deposits accumulate within the arterial walls, causing the arteries to become hardened and narrowed. Severe calcification poses challenges during angioplasty procedures by limiting the ability to fully expand the artery and increasing the risk of complications such as dissection or inadequate stent deployment.
Causes of Coronary Artery Calcification
- Atherosclerosis: Buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arterial walls, which may become calcified over time.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Elevated levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood, leading to increased arterial calcification.
- Age and Lifestyle Factors: Older age, smoking, hypertension, and diabetes are risk factors associated with accelerated arterial calcification.
Indications for Rotational Atherectomy
Rotational Atherectomy may be recommended for patients who have:
- Severely Calcified Coronary Arteries: Detected during diagnostic angiography or imaging studies, indicating significant plaque burden.
- Failed Angioplasty: Inadequate plaque modification or vessel preparation with conventional angioplasty techniques due to severe calcification.
- High-Risk Lesions: Complex coronary lesions with calcified nodules or heavily calcified segments that pose challenges for optimal stent deployment.
Components of Rotational Atherectomy Device
A Rotational Atherectomy device consists of:
- Rotablator Catheter: A thin, flexible catheter with a diamond-coated burr at its tip, connected to a motorized console.
- Motorized Console: Controls the rotation speed and direction of the burr, enabling precise plaque removal.
- Guide Wires and Support Catheters: Used to guide and support the Rotablator catheter during the procedure.
Rotational Atherectomy Procedure Overview
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before undergoing Rotational Atherectomy, patients typically undergo:
- Diagnostic Angiography: To visualize the coronary arteries and identify the location and severity of calcified lesions.
- Medical Evaluation: Including assessment of cardiac function, blood tests, and discussion of the procedure risks and benefits.
Procedure Steps
- Anaesthesia: Local anaesthesia is administered to numb the insertion site, often in the groin or wrist, where a sheath is placed to access the arterial system.
- Guidewire Placement: A specialized guidewire is advanced through the coronary artery to the site of the calcified lesion under fluoroscopic guidance.
- Rotablator Catheter Insertion: The Rotablator catheter, with its diamond-coated burr, is carefully advanced over the guidewire to the calcified lesion.
- Plaque Removal: The Rotablator burr is activated and rotates at high speeds (up to 200,000 revolutions per minute), effectively grinding away the calcified plaque while preserving the integrity of the arterial wall.
- Debris Management: Saline irrigation and aspiration catheters are used to flush out debris generated during plaque removal, minimizing the risk of distal embolization.
- Assessment and Post-Dilatation: Post-rotational atherectomy, the artery is reassessed with angiography to evaluate plaque modification and determine the need for additional treatments such as balloon angioplasty or stent placement.
Recovery and Hospital Stay
- Immediate Post-Procedure: Patients are monitored in a cardiac care unit or recovery area to assess for complications such as bleeding, vascular injury, or arrhythmias.
- Hospital Stay: Most patients require an overnight stay for observation and monitoring of cardiac enzymes and vital signs.
Benefits of Rotational Atherectomy
- Effective Plaque Modification: Removes calcified plaque, enabling better vessel expansion and optimizing outcomes of subsequent interventions.
- Improved Procedural Success: Facilitates successful stent deployment and reduces the risk of complications associated with inadequate lesion preparation.
- Symptom Relief: Alleviates symptoms of angina and improves exercise tolerance in patients with severely calcified coronary arteries.
Conclusion
Rotational Atherectomy is a specialized procedure that plays a crucial role in managing severe coronary artery calcification and optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing coronary intervention. Dr Ankeet Dedhiya and our team of experienced interventional cardiologists are dedicated to providing personalized care and utilizing advanced technologies to improve heart health and quality of life. Whether you are considering treatment options or preparing for Rotational Atherectomy, we are committed to supporting you throughout your cardiac care journey.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Rotational Atherectomy is a procedure to remove severe calcified plaque from coronary arteries using a diamond-coated burr, improving blood flow and preparing the artery for angioplasty and stent placement.
Patients with severely calcified coronary arteries, failed angioplasty attempts, or high-risk lesions with heavy calcification may need Rotational Atherectomy.
Coronary artery calcification is caused by atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, aging, smoking, hypertension, and diabetes.
The procedure includes local anesthesia, guidewire placement, insertion of the Rotablator catheter, high-speed plaque removal, debris management, and post-procedure assessment.
The procedure effectively modifies calcified plaque, enhances vessel expansion, improves stent deployment, and relieves symptoms of angina.
Potential risks include vascular injury, coronary perforation, and arrhythmias. However, it is generally a safe procedure with careful monitoring.
